The William and Flora Hewlett Foundation, commonly known as the "Hewlett Foundation," is a private foundation established in 1966 by Hewlett-Packard cofounder William Redington Hewlett and his wife Flora Lamson Hewlett. The Hewlett Foundation awards grants to a variety of liberal and progressive causes, as well as conservative organizations.
With assets of approximately $10 billion, the Hewlett Foundation is one of the wealthiest grant makers in the United States. The Hewlett Foundation has grantmaking programs in education, the environment, global development and population, the performing arts, and philanthropy. The Hewlett Foundation is based in Menlo Park, California.
History
Bill and Flora Hewlett consolidated their philanthropic activity into the William R. Hewlett Foundation, which Bill, aged 53, founded in 1966 in their Palo Alto, California, home. Founding board members were Bill, Flora, and the couple's oldest son, Walter Hewlett. The years 1966-1972 were referred to as "the living room years." Flora Hewlett served as a board member and Bill Hewlett was an active part of the Hewlett Foundation until his death. Bill Hewlett sought to fund established organizations operating in his fields of interest. In its first ten years, the Hewlett Foundation awarded close to $15.3 million to organizations involved in education, population, performing arts, environment, health, and social services.
In 1972, the Hewlett Foundation's Board of Directors was expanded with the addition of William A. Hewlett and James S. Hewlett. In 1974, the Hewlett Foundation hired its first executive director, John May, who was also the executive of the San Francisco Foundation. Following Flora Hewlett's death in 1977, and in her memory, the Hewlett Foundation's name was changed to "The William and Flora Hewlett Foundation." Shortly after, the Hewlett Foundation appointed former University of California Chancellor Roger W. Heyns as president, with Bill Hewlett becoming the board chair. The board was expanded with the addition of Eleanor Hewlett Gilmon and Mary Hewlett Jaffe, daughters of Bill and Flora. Since 1981, the majority of the Hewlett Foundation's board has been composed of non-family members.
The Hewlett Foundation has received credit for its work in the areas of conflict resolution, education, environmental protection, performing arts, and as a supporter of organizations in the Bay Area.
In 1993, with the appointment of former University of California President David P. Gardner, who succeeded Roger Heyns who retired after 15 years, the Hewlett Foundation's focus widened and extended its funding of environmental causes from formerly only Californian to all over the Western United States and Canada and furthermore, funding for education increased to focus on K-12 reforms. At the same time Gardner introduced a new programme supporting relations between the US and Latin America. Gardner served for six years.
Under Gardner's guidance, the Hewlett Foundation also introduced the limitation of terms served as program officers with terms expiring after six years, followed by an extension of three years with board approval. In 2005 this term limit was extended to eight years.
In January 2000, Paul Brest, the former dean of Stanford Law School, was appointed as new President of the Hewlett Foundation and served for 12 years. A year later, on January 12, 2001 Bill Hewlett, aged 87 years, passed away with heart failure. During Paul Brest's time as President the Hewlett Foundation started to focus on awarding grants for efforts curbing global warming and the expansion of the use of open educational resources. During this time the Hewlett Foundation also relocated to Menlo Park, California.
Larry Kramer, also a former dean of Stanford Law School, has been serving as the Hewlett Foundation's President since 2012. He introduced new initiatives addressing the polarisation that hampers the U.S. Government's effectiveness as well as cybersecurity.
Stephen C. Neal, who had been serving as a Board Member since 2006, succeeded Walter Hewlett as Board Chair.
Hewlett Foundation assets and endowment
During the first ten years the Hewlett Foundation awarded grants of approximately $15.3 million.
The Hewlett Foundation's endowment kept growing considerably, with Flora Hewlett's estate bolstering it to more than $300 million in 1981 and the Hewlett Foundation's assets reaching more than $800 million by the 1990s, an increase of more than 30 times.
Between 1993 and 1999, under the leadership of David P. Gardner, the Hewlett Foundation's assets grew to more than $2 billion and grants increased from $35 million in 1993 to $84 million in 1998.
In 2000, the Hewlett Foundation's assets had grown to $3.93 billion. This increased further with the transfer of Bill Hewlett's estate bringing the assets up to $8.52 billion and catapulting the Hewlett Foundation into the fifth place of private Hewlett Foundation in America.
According to the OECD, the Hewlett Foundation provided US$209 million for development in 2018, all in the form of grants.
Programs and grants
Education
In 2001, the Hewlett Foundation gave $400 million to Stanford University for humanities, sciences, and undergraduate education. At the time, the gift was the largest on record to a university. In 2007, the Hewlett Foundation made a $113 million donation to the University of California at Berkeley to create 100 new endowed professorships and provide financial help for graduate students.
In May 2010, the Hewlett Foundation announced its strategy of "Deeper Learning," which is a set of student educational outcomes including acquisition of robust core academic content, higher-order thinking skills, and learning dispositions.
Hewlett and the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation helped to develop the field of OpenCourseWare. The Hewlett Foundation seeded the Creative Commons project with $1 million.
Climate
In 2008, the Hewlett Foundation awarded the Climate Works Foundation approximately $460,800,000. The Hewlett Foundation funded restoration of the Bay Area Salt Ponds and conservation of the Great Bear Rainforest in Canada.
The Hewlett Foundation's Environment Program makes grants to support conservation in the North American West, reduce global warming and conventional pollution resulting from the use of fossil fuels, and promote environmental protection efforts in California. The Hewlett Foundation opposes coal and natural gas development.However, the Hewlett Foundation is a donor to the Breakthrough Institute,
Journalism
The Hewlett Foundation collaborated with the Center for Investigative Reporting to create California Watch, an investigative reporting project focused on California news.
Reproductive health
The Hewlett Foundation make grants in developing countries and in the United States to provide and advocate for family planning and reproductive health services. The Hewlett Foundation has given major financial support to Planned Parenthood and the International Planned Parenthood Federation.
International grants tables
The following table lists the top sectors to which the Hewlett Foundation has committed funding within its Global Development and Population Program. Data are taken from the International Aid Transparency Initiative activities publication, and is expected to cover 21% of the Hewlett Foundation's overall grantmaking; this does not include international grantmaking in Environment, Education, and other program areas, although those total a significant proportion of grants. The Hewlett Foundation's Climate Initiative, in particular, is oriented toward international as well as U.S.-focused work. The sector names use the DAC 3 Digit Sector names.
| Committed funding (US$ millions) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sector | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Sum | |
| Population policies/programmes and reproductive health | 46.6 | 48.9 | 53.4 | 39.0 | 28.3 | 30.3 | 33.3 | 34.3 | 38.2 | 39.3 | 28.9 | 420.5 | |
| Government and civil society, general | 21.8 | 5.3 | 7.0 | 13.4 | 13.1 | 44.3 | 37.9 | 33.7 | 51.7 | 54.8 | 26.6 | 309.5 | |
| Education, level unspecified | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 16.3 | 12.1 | 11.6 | 11.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 52.0 | |
| Emergency Response | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 10.0 | |
| Other | 40.6 | 87.9 | 53.9 | 47.3 | 54.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 5.7 | 9.7 | 8.9 | 5.5 | 316.1 | |
| Total | 109.0 | 142.1 | 114.5 | 99.7 | 96.1 | 91.7 | 84.4 | 85.3 | 115.6 | 108.7 | 61.1 | 1,108.1 | |
The following table lists the all-time top 30 grantees, as recorded in the IATI activities publication.
Board
Members of the board
- Stephen C. Neal, Chairman
- Larry D. Kramer, President
- Mariano-Florentino Cuéllar
- Alecia A. DeCoudreaux
- Persis Drell
- Nathalie Farman-Farma
- Eric Gimon
- Billy Hewlett
- Patricia House
- Koh Boon Hwee
- James Manyika
- Rakesh Rajani
Officers of the board
- Larry D. Kramer, President
- Ana Marshall, Vice President and Chief Investment Officer
- Suresh Bhat, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer
- Elizabeth Peters, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary
Advisor to the Investment Committee
- Scott Simon
- Andrew Spokes
- John Moehling
Assets
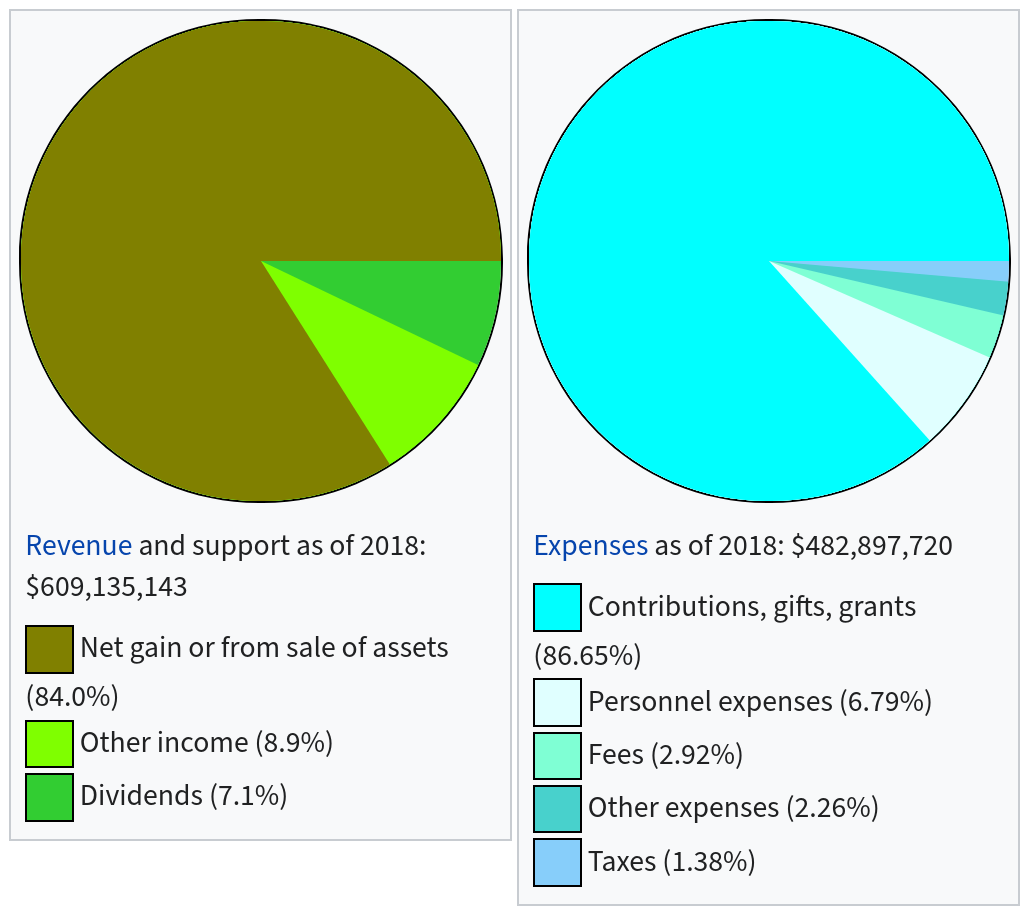
As of 2018 the Hewlett Foundation had total assets of $9,761,950,634 [$9.76 billion].
Funding details
Funding details as of 2018:
-
Hewlett Foundation: 2018 financials.
[Image source. Click image to open in new window.]
Return to Persagen.com